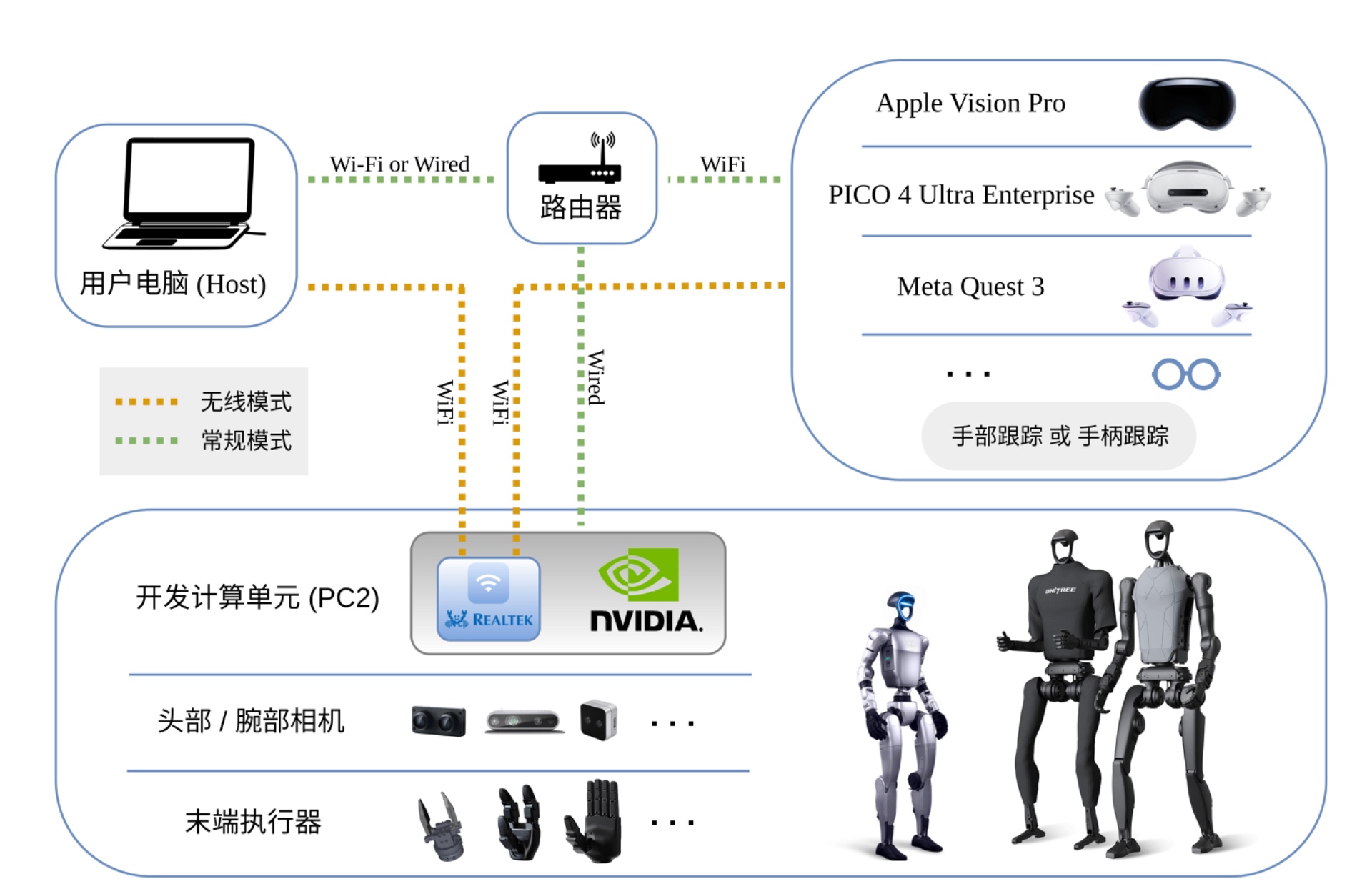
提供最先进的智能机器人科研平台,助力高校用户发文章和申请项目
Apple Vision Pro遥操作核心是依托眼动+手势+语音的原生交互,结合WebXR/网络通信,实现对设备、机器人等的远程精准控制。核心原理:Vision Pro手势追踪捕捉动作,经WebXR传输至机器人端,结合逆运动学与图像推流,实现实时控制与视觉反馈。应用场景包括• 工业/科研:远程操控机械臂、人形机器人,完成危险/精细作业。• 智能家居:通过Vision Pro控制智能家电,实现沉浸式家居控制。• 医疗:辅助远程手术、康复机器人操控,提升医疗服务可达性。
效果演示
本例程在 Ubuntu 20.04 和 Ubuntu 22.04 操作系统下进行测试。在其他版本的操作系统上构建时,所需条件和步骤可能会与本文档描述的存在差异。您可以根据实际使用情况调整构建过程。
该部分用于配置人形机器人 H1 双臂(共14个自由度)的末端位姿逆运动学求解相关的软件库。Apple Vision Pro 获取左右两个手腕位姿后,使用 pinocchio 和 CasADi 库加载 URDF 并进行逆运动学计算,求解出到达该位姿的关节电机角度值。 meshcat 库则用于调试时在 Web 端进行可视化显示。
conda create -n tv python=3.8 conda activate tv conda install pinocchio -c conda-forge pip install meshcat
注意
使用 pip 安装的 pinocchio 有可能不是最新版本 3.1.0,本环境需要使用 3.1.0 版本,请仔细检查。
必须先安装 pinocchio 并确保安装成功,然后再进行 TeleVision 的环境配置。安装顺序颠倒可能导致会安装好的 TeleVision 环境出错。
下文所有终端命令都应该在 conda 的 tv 环境内执行,除非另有说明。
该部分用于配置计算机主机与人形机器人的 unitree_dds_wrapper,可以使用 python 实现主机和机器人之间的通信、控制。请执行下面命令进行安装:
# 安装python版本的 unitree_dds_wrapper git clone cd unitree_dds_wrapper/python pip3 install -e .
本例程在 TeleVision 开源项目基础上修改完成,下述部分配置也可参考该项目的 README 及相关页面。在此,Isaac Gym 仿真环境用于测试配置正确性。
使用 git 克隆本项目至本地后,进入到项目路径下,安装基本功能库:
cd ~ git clone cd avp_teleoperate pip install -r requirements.txt
在 Isaac Gym 下载页面下载 Isaac Gym 安装包并解压,然后到 IsaacGym_Preview_4_Package/isaacgym/python 目录下执行下面命令:
pip install -e .
安装brew
sudo apt-get install build-essential procps curl file git cd ~ /bin/bash -c ""
当要求输入回车键时,请按下回车。然后继续执行:
echo 'eval "$(/home/linuxbrew/.linuxbrew/bin/brew shellenv)"' >> $HOME/.bash_profile
配置环境变量
eval ""
使用 brew 安装mkcert
brew install mkcert
查看本机 IP 地址
ifconfig | inet
假设本机 IP 地址是192.168.123.2
创建证书
mkcert -install && mkcert -cert-file cert.pem --file .pem localhost 127.0.0.1
把生成的 cert.pem 和 key.pem 两个文件拷贝到项目的 teleop 目录下:
cp cert.pem key.pem ~/avp_teleoperate/teleop/
系统防火墙设置
sudo ufw allow
在 Apple Vision Pro 中安装证书
mkcert -
上面命令可以获取到 rootCA.pem 的路径。然后通过苹果的隔空投送功能把 rootCA.pem 文件发送到 Apple Vision Pro。
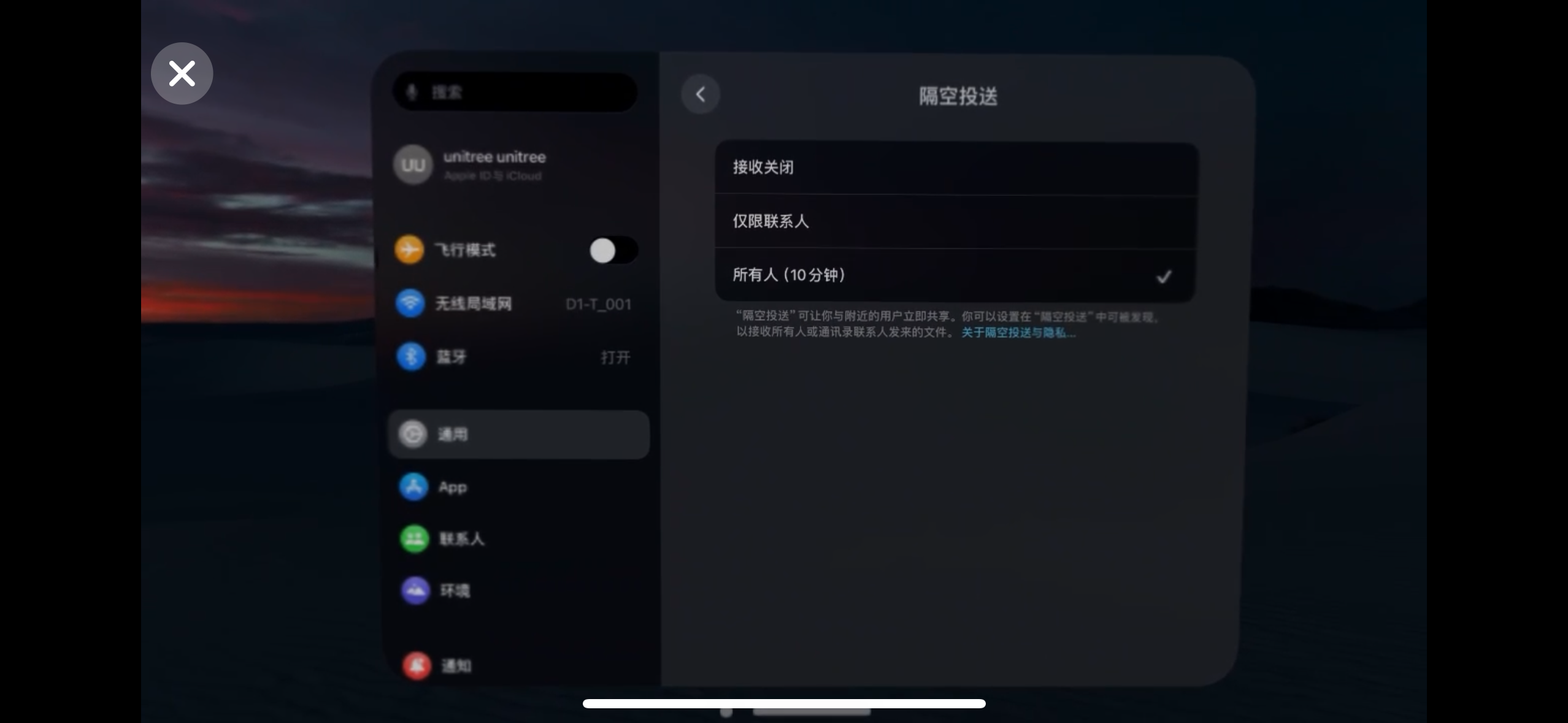
注意:Apple Vision Pro 接收文件前需要启动文件接收功能,方法是:设置 >> 通用 >> 隔空投送 >> 所有人(10分钟)。
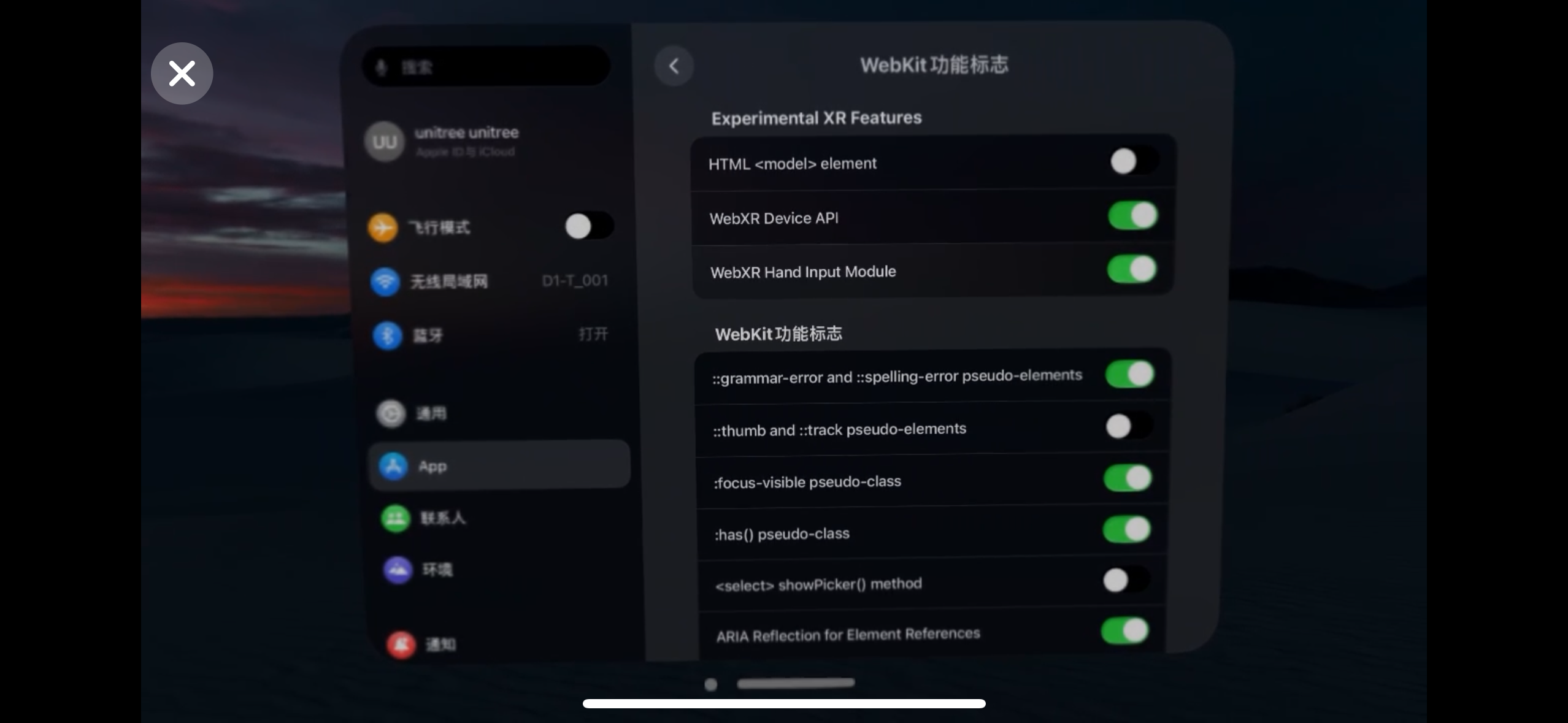
设置 >> Apps >> Safari浏览器 >> 高级 >> 功能标志 >> 启用 WebXR 相关功能。
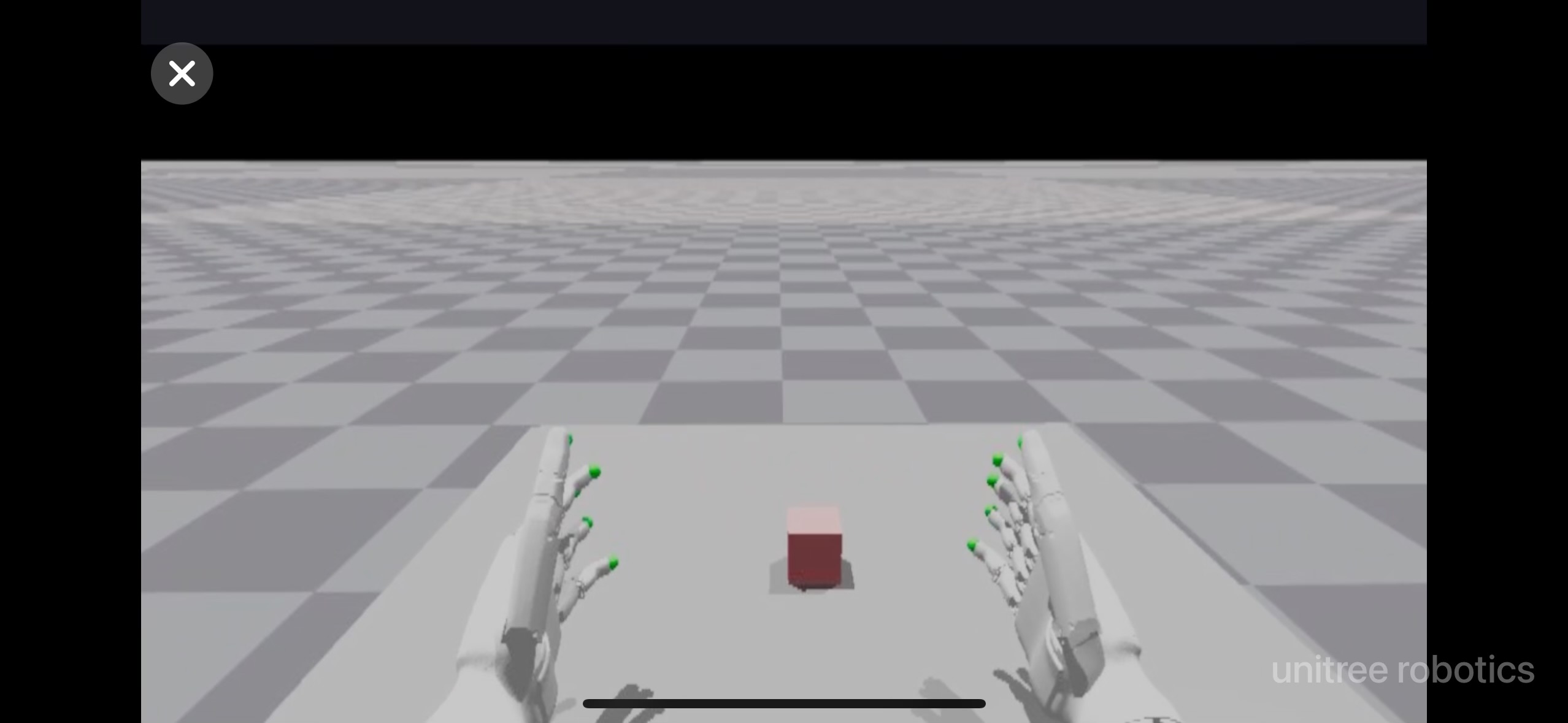
~/avp_teleoperate/teleop python teleop_hand.py
打开 Apple Vision Pro 的浏览器输入 https://192.168.123.2:8012?ws=wss://192.168.123.2:8012
点击 "Enter VR" 并且允许跟踪,就可以看到如下画面:

如果使用真实遥操模式,需确保人形机器人 Unitree H1_2 的硬件活动范围内不会碰撞到人或其他物品,以免发生意外;
人形机器人 Unitree H1_2 可使用吊起或者端坐(如本文档 效果演示 一节所示)的方式摆放,避免双臂活动范围内有明显的碰撞物出现;
操作人员应正确佩戴 Apple Vision Pro 设备,并遵循上述软件配置;
双目相机的主要作用是辅助操作人员,通过 Apple Vision Pro 观看到机器人视角下工作空间的视野。为了获得最佳效果,请根据所使用的相机型号和所需的工作空间视野,适当调整相机的安装位置和朝向。
在执行遥操作的程序前,需要预先启动一些服务支撑的程序。
可以参考 灵巧手开发 配置相关环境和编译控制程序。首先到 该网址 下载灵巧手控制接口程序并将之拷贝到 机器人 Unitree H1_2 的 PC2 中。在 PC2 中解压完成后,使用下述命令进行编译:
sudo apt install libboost-all-dev libspdlog-dev # Build project cd h1_inspire_service & mkdir build & cd build cmake .. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release make # Terminal 1. Run h1 inspire hand service sudo ./inspire_hand -s /dev/ttyUSB0 # Terminal 2. Run example ./h1_hand_example
如果发现左右灵巧手所有手指不断循环张开、闭合动作则表示成功。确认成功后,关闭 Terminal 2 中的 ./h1_hand_example 程序即可。
把 avp_teleoperate/teleop/image_server 目录中的 image_server.py 拷贝到机器人 Unitree H1_2 的 PC2 中,并在 PC2 内执行下面命令:
sudo python3 image_server.py
注意:这里需要检查 OpenCV 读取图像时的参数是否与双目相机硬件匹配,以及对于推流使用的默认5555端口是否可用。
图像推流服务开启以后,可以在主机终端使用 image_client.py 测试通信是否成功(测试成功后记得关闭该程序):
python image_client.py
注意1: 所有人员一定要与人形机器人之间保持充足的安全距离,以免发生危险和意外!
注意2: 在使用本程序并进行启动时,必须确保输入的参数和操作流程是正确的,并对程序可能会执行的各种行为结果有充分预期!
python teleop_hand_and_arm.py # 程序启动后,如果配置正确,终端最终输出 `Please enter the start signal (enter 's' to start the subsequent program):` 信息。 # 此时,佩戴 Apple Vision Pro 的操作人员应将手臂形状摆放为与 Unitree H1_2 初始姿态相接近的姿势,避免初始位姿差距过大导致机器人产生过大的摆动。 # 当操作人员姿势摆放好后,主机操作人员可按下 `s` 字母和回车键,正式启动遥操作程序。这时,机器人双臂便可跟随佩戴 Apple Vision Pro 的操作人员双臂移动。
代码的整体结构与 TeleVision 保持一致,此处只着重介绍与 Unitree Robot 相关的文件目录
avp_teleoperate/ │ ├── act 存放模仿学习策略相关文件 │ ├── assets 存放机器人 URDF 相关文件 │ ├── scripts 存放一些工具类文件 │ ├── teleop 存放遥操作主要文件 │ │ │ ├── image_server/ 图像推流服务端与客户端相关代码 │ │ | │ │ ├── image_client.py 客户端(仅用于测试 Unitree H1_2 上的图像推流服务是否正常) │ │ | │ │ ├── image_server.py 服务端(捕获相机的图像并通过网络对外发送,该代码在 Unitree H1_2 上运行) │ │ │ ├── robot_control/ 存放IK解算、手臂控制相关文件 │ │ | │ │ ├── robot_arm_ik.py 双臂IK解算代码 │ │ | │ │ ├── robot_arm.py 双臂控制代码 │ │ | │ │ ├── robot_hand.py 机械手控制代码 │ │ │ │──teleop_hand_and_arm.py 遥操作的启动程序代码 │ │ │ │──teleop_hand.py 可用于测试环境配置
1.请务必按照本文档的要求安装硬件设备、连接线缆;
2.在遥操过程中,请务必避免遥操作时机器人双臂的活动轨迹重合导致的碰撞!确保机器人硬件活动范围内不会碰撞到人或其他物品,以免发生意外;
3.在使用例程时,必须确保输入的参数和操作流程是正确的;
4.机器人在运行过程中会产生热量,在运行或刚停止时,请不要触摸电机关节部位;
5.例程使用结束后,请务必关闭例程并断电;
Q: 双目相机可以换为其他型号吗?
A: 任意型号 USB 免驱动双目相机均可(推荐使用 FOV 较大的相机,保证操作时充足的视野)。新相机可通过 teleop/image_server/ 下的客户端 image_client.py 和服务端 image_server.py 程序进行测试。
Q: 其他人形机器人可以使用该例程吗?
A: 不可以直接使用,但可以借鉴。包括但不限于修改 URDF、IK 解算程序以及关节映射等代码。
Q: 遇到运行错误 AttributeError: type object 'Callable' has no attribute...,怎么办?
A: 可以尝试使用命令 pip uninstall typing 解决
Q: 双臂可以进行遥操作,但是灵巧手却不会动,怎么办?
A: 程序中,双臂和灵巧手的控制指令是分开的。先通过 开启灵巧手服务 小节内容中所述的 h1_hand_example 程序检测灵巧手是否正常工作。如果没有正常操作,请参考 灵巧手开发 页面或联系灵巧手相关的技术支持。


 Donghu Robot Laboratory, 2nd Floor, Baogu Innovation and Entrepreneurship Center,Wuhan City,Hubei Province,China
Tel:027-87522899,027-87522877
Donghu Robot Laboratory, 2nd Floor, Baogu Innovation and Entrepreneurship Center,Wuhan City,Hubei Province,China
Tel:027-87522899,027-87522877