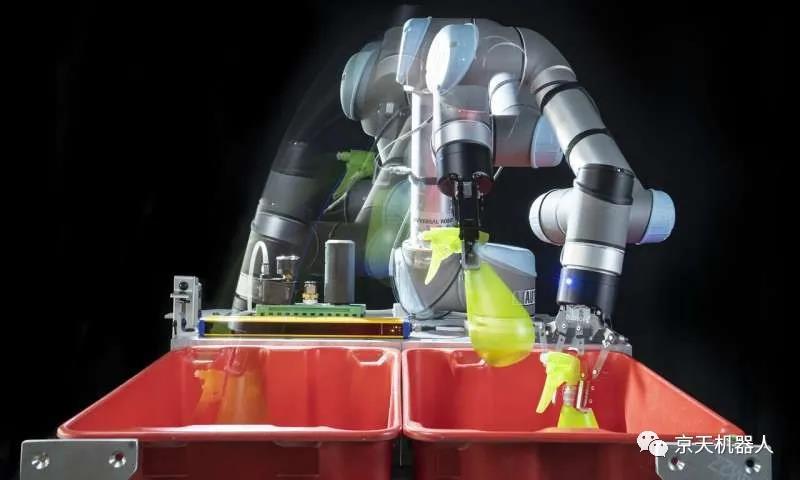

Over the past year, lock-in measures and other COVID-19 security measures have made online shopping more popular than ever, but the soaring demand has made it difficult for many retailers to fulfill orders while ensuring the safety of warehouse employees.
Researchers at the University of California, Berkeley have developed new artificial intelligence software that enables robots to quickly and skillfully grasp and move objects smoothly, allowing them to help people in warehouse environments in the near future. This technology is described in a paper published online today (Wednesday, November 18) in the journal Scientific Robots.
Automated warehouse tasks can be challenging because humans naturally take many actions, such as determining where and how to pick up different types of objects, and then coordinating the shoulders, arms, and arms required to move each object from one location to another. And wrist movement. It is quite difficult for robots. Robot actions also tend to be blunt, which may increase the risk of damaging products and robots.
Ken Goldberg, Distinguished Professor of Engineering at the University of California, Berkeley, said: “Warehouses are still mainly operated by humans, because robots still have difficulty reliably grasping many different objects.” “In the car assembly line, the same is repeated again and again. In this way, it can be automated. But in the warehouse, every order is different."
This video demonstrates the pick and place performance of warehouse robot arms before and after applying deep neural networks.
In earlier work, Goldberg and Jeffrey Ichnowski, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of California, Berkeley, created a "grass-optimized motion planner" that can calculate how the robot picks up objects and how they move to transfer objects from one location to another. A location.
However, the actions generated by this planner are a bit jerky. Although the parameters of the software can be adjusted to generate smoother motion, these calculations take about half a minute on average to calculate.
In this new study, Goldberg and Ichnowski collaborated with graduate student Yahav Avigal and undergraduate student Vishal Satish at the University of California at Berkeley to greatly shorten the calculation time of the exercise planner by integrating deep learning neural networks.
Neural networks allow robots to learn from examples. Later, robots can usually be generalized to similar objects and movements.
However, these approximations are not always accurate enough. Goldberg and Ichnowski discovered that a motion planner can be used to optimize the approximation generated by a neural network.
Ichnovsky said: "The neural network only takes a few milliseconds to calculate an approximate motion. This is very fast, but it is not accurate." "But if we then input the approximate value into the motion In the planner, the motion planner only needs to perform a few iterations to calculate the final motion."
By combining the neural network with the exercise planner, the team reduced the average calculation time from 29 seconds to 80 milliseconds, or less than a tenth of a second.
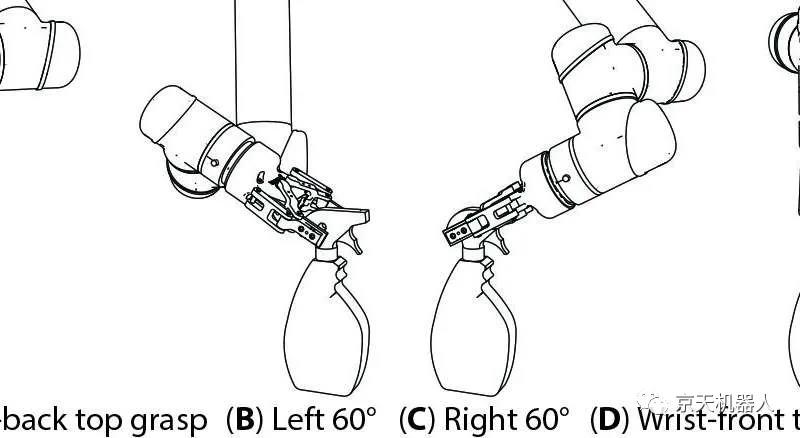
The motion planner optimized for deep learning also allows the robot to perform more motions.
Goldberg predicts that with this and other advancements in robotics, robots will assist the warehouse environment in the next few years.
Goldberg said: “Due to COVID-19, the way to buy groceries, medicines, clothing and many other things has changed, and people may continue to shop in this way even after the pandemic is over.” “This is robots for humans. Workers provide new opportunities for support.

Donghu Robot Laboratory, 2nd Floor, Baogu Innovation and Entrepreneurship Center,Wuhan City,Hubei Province,China
Tel:027-87522899,027-87522877
Robot System Integration
Artificial Intelligence Robots
Mobile Robot
Collaborative Robotic Arm
ROS modular robot
Servo and sensor accessories
Scientific Research
Professional Co Construction
Training Center
Academic Conference
Experimental instruction
Jingtian Cup Event